Testing body composition
Body composition, the measure of fat mass to lean tissue including bone, muscle, ligaments, tendons and organs is an important metric. One of the approaches is the two component system. It divides body up into lean body mass and stored fat. The lean body mass is not free of fat. It contains essential fat which is a constant component of a body and its quantity does not often change. The notions of lean body mass and fat free body mass are not interchangeable. If the quantity of essential fat is derived from lean body mass we will get the value of fat free body mass.
Stored fat is accumulated under the layer of skin and around viscera. Its quantity depends on eating habits; way of life, physical activity types, and it evidently may change throughout of our life.
The multi component approach divides lean body mass into muscles, bones and other tissue weight.
The health centred method focuses on body fat percentage or examines relative fat. In sport- anthropometry to know the rate of muscle tissues is also considered important. It means that if a person is less fit it covers high amount of fat. In contrast with this low amount of fat and lots of muscles it means ideal fit conditions. Body composition test is also used in recreation.
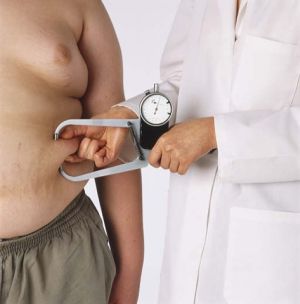
A skin calliper device is used to measure (Mészáros, 1990) the thickness of the skin for each site (see table 6). Each protocol has specific sites for testing spread across the body commonly including the chest, arm, abdominal and thigh. After plugging the numbers into a formula body composition can be estimated.
Males:
F% = 3,7234 + 0,1999×CR + 0,2876×HR - 0.0209×CSR - 0,0054×LPR ± 3,93
Females:
F% = 9,0075 + 0,1769×HR + 0,2327×CSR + 0,2249×LPR+ 0,0542×TRR ± 4,49
F% ═ body fat in body mass percentage, ═ thigh folds, ═ abdominal folds, ═ hip folds, ═ triceps in mm.
As the thickness and composition of a body of males and females are different two formulas should be used. Generally a man’s body has 12 – 15% fat and 45 – 50% muscle, while a female’s body contains 20 – 25 % fat and 40% muscle.
Mészáros and co-workers (1990) have come up with several other formulas. What they have in common is the data of bone width are used for estimating bone mass as well as for calculating muscles the data of limbs are needed (Boldizsár, 2004).
The model of four anthropometric fraction body mass of Drinkwater and Ross (1980) assessed the quantity of absolute subcutaneous fat by measuring four skin folds each on the trunk. The measured and gained data are compared with those of unisex human phantom (Boldizsár, 2004).
The methods of DEXA (Dual- energy X- ray absorptiometry), MRI and CT are also widely used. BIA – bioelectronical impedance analysis is considered one of the most reliable methods of screening body fat. BIA measures the impedance or resistance to the signal as it travels through the water found in muscles fat. The more muscle a person has the more water his/her body can hold. Actually it determines the electrical impedance, or opposition to the flow of an electric current through body tissues which can be used to estimate total body water. And with these data fat-free body mass and body fat can be estimated (Kyle, 2004).
BIA based examination is done by InBody composition analysers. Using the method of quantitative elements of body composition provides basic information required assessing the status of the body. The software compares the data of adults with international standard outcomes and in case of 18 year old persons series of percentile curves are used. The simple two electrode method measures only the relative quantity of body fat. The four-electrode InBody devices can diagnose obesity (body mass index, waist hip ratio). They show BMR – Basal Metabolic Rate and provide a detailed report of individuals’ measurements, such as, total body water, total body fat percentage, bone mineral content etc. The software of the latest devices provides data about ideal body mass as well as offers training programmes.