VIII.3.1. Measurements at rest before loading
The examination of individuals’ and athletes’ health is suggested before loading tests.
A few questions may help collecting data, but more time should be needed if we check blood pressure and measure pulmonary functions.
- Pulmonary function test. The most often applied test is the vital capacity (VC) test which measures the quantity of exhaled air after maximal inhalation. High vital capacity is typical of sports requiring great stamina and endurance. The other two parameters are the maximal voluntary ventilation (MVV) and the first seconds of forced expiratory values (FEVI%).
- Heart rate at rest itself indicates well how healthy and fit people are. The normal value of heart rate at rest is 70 beats/ minute, but it can also be 40 beats/ minute while children’s heart beats more per minute at the age of 12 and their heart rate is 80 beats/ minute.
The most often used method of calculating maximal heart rate is a simple formula, that is, HRmax ═ 220 – age.
Karvonen formula is applied to measure heart rate under different loadings and it is helped through calculating maximal heart rate at rest.
- Body composition is used to describe the relative ratio of certain body components and tissues in relation to global body mass. It measures the percentage of body fat, muscle, bone and water of human body. In sport-anthropometry fat- and muscle ratio are also important. If the fat ratio is high and at the same time the muscle mass percentage is low it indicates poor fitness. In contrast to this if the fat ratio is low and the muscle mass rate is high it means ideal fitness status. Nowadays the determination and estimation of body composition in recreation and competitive sports is a popular approach as it supports preparation and maintains the stability of health. János Mészáros’ work (1990) summarizes the traditional methods and techniques of estimating the percentage of muscle mass and body fat. He describes, for example, the measuring methods of subcutaneous fat thickness.
- The so called InBody technology, based on the theory of bio-impedance, is applied to measure body composition. Body water, proteins, minerals and body fat, which are the components of human body closely relate to the status of our health. BIA body composition analyzer determines the electrical impedance, or opposition to the flow of an electric current through body tissues. Then it can be used to calculate an estimate of total body water. The other crucial factor of the electric conductivity of tissues is the form of tissues. The rounder the form of cells the worse their impedance is. When fat tissues contain little water and they have round forms their impedance is poor compared to the other body tissues. In contrast to this the impedance of fat free tissues, which have high water content and longitudinal fibrous elements, is high. By using the impedance measurements along with a person’s height and weight, and body type (gender, age, fitness level) it is possible to calculate the percentage of body fat, fat-free mass, and other body composition values.
- Body mass index (BMI) or Quetelet index is a value derived from individuals’ mass, weight and height. This method was developed by the Belgian Adolphe Quetelet in the middle of 1800s. BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body and is universally expressed in units of kg/m2. It attempts to quantify the amount of individuals’ tissue mass, and then categorize these people as underweight, normal weight, overweight and obese. This method is used for predicting both children’s and adults’ health status. As it is an easy method it is often used also to estimate their obesity level.
Many athletes may have a BMI that is misleadingly high, relative to their percent body fat. Although it does not show the actual body fat percentage still it can be very useful when calculating an individual’s healthy weight.
On the basis of BMI “number” adults’ leanness and obesity rates are estimated by using WHO protocol (Table 3). The current value recommendations are:
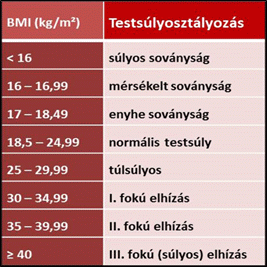
Table 3. http://www.calculator.net/bmi-calculator.html
The following chart (diagram 4) helps estimating BMI. The vertical axis (m) shows height and the horizontal axis indicates body mass (kg). Colours are used to differentiate among categories.
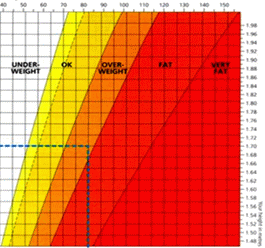
These categories cannot be used for estimating children’s BMI. A percentile chart is applied which indicates what percentage of children have lower BMI. They are in the same age and have the same sex compared to the children’s values who participated in the examination. BMI 50 suggests average weight, 97 percentile upwards indicates obesity and percentile below 3 shows considerable weight shortage.
See the data of KSH Népességtudományi Kutatóintézet
- Waist - hip ratio is the ratio of the circumference of the waist and hips. It is calculated as waist measurement is divided by hip measurement. Waist is measured at the smallest circumference of the natural waist just above the belly bottom, and hip circumference is measured at its widest parts of the buttocks. WHO states that abdominal obesity is defined as a waist-hip ratio above 0.90 for males, and above 0,85 for females, and these data indicate obesity. Fat accumulation is a marker of medical risks.
- Physique is the shape, size and stature or appearance of human body. It is the total inherited and acquired somatic attributes of individuals. Genetics determines human skeletal as well as the quantity of muscle-fat tissues. It reveals the fitness and health status of a person. An athlete’s physique is well proportioned, muscular and sporty unlike that of the people who neglect physical activity. The determination of a person’s physique is called somatotype measurement. The method of Heath-Carter is widely used in the world. On the basis of different tissue types (fat, muscle, bone) and the dominance of certain body systems this method differentiates the following physique components: endomorph, mezomorph and ektomorph (table 5). Each component is expressed with numbers in a scale ranging form 1 to 7. Accordingly endomorph type scores 7-1-1, mezomorph type is characterized with 1-7-1 and ectomorph type with 1-1-7. The number group of 4-4-4 indicates average physique.
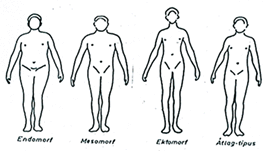
Table 5.
These variations are located on the tips of a triangle. As with these three variations various body types can be described.
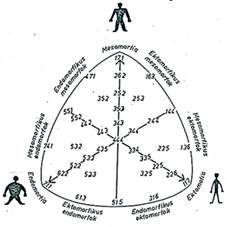 Table 6. Somatotyping
Table 6. Somatotyping
Somatotype is the measurement of body shape and size, fat fold thickness as well as elbow and knee width. In each of this category people are classified on a scale ranging from 1 to 7. The three numbers together give a somatotype number.
We should bear in our mind that the previously mentioned human-biological and antropometrical character measurement techniques are only one possible way of choosing sports. Athletes need flexibility, endurance, speed, force and appropriate reaction time, life style, nutrition and health status to opt for a sport that suits them. We should bear in our mind that proper physique, ideal body composition and BMI tests do not serve enough data for trainers and instructors.