VI.2.1. The notion of hiking
People, when getting away from their civilizational environment often spend their free time in nature by doing physical activities at more or less difficult grounds. In the meantime they improve their motor skills, personality and aesthetic responsiveness.
https://hu.wikipedia.org/wiki/Term%C3%A9szetj%C3%A1r%C3%A1s
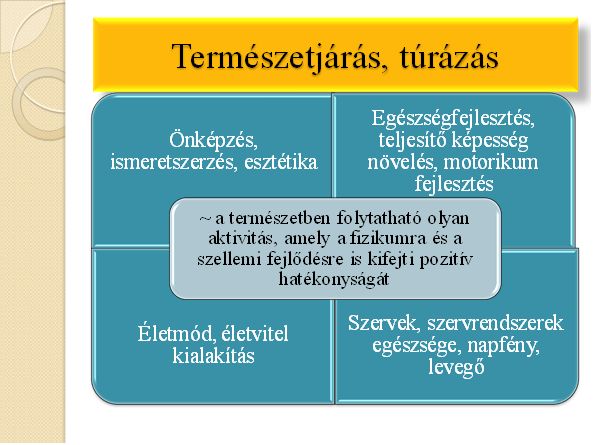
Figure 1.Nature walking, hiking, personality (own source)
It is an activity which can be done in nature, which has a positive effect on the person’s physical and intellectual properties. Autonomous learning, health improvement, improved performance, improved motor skills.
Healthy organs and systems of organs, sunshine, clean air
Lifestyle, way of living
Acquisition of knowledge, autonomous learning, aesthetics
Classification of hikes by difficulty (by Damilano és Gardien (2005)
- Easy, short hike. Lasts 1-2 hours, the distance covered is 3-6 kilometres. There are clear tourist paths leading to some sight. The walk is playful and joyful.
- Hike of medium difficulty. Good and careful planning is needed, physically more strenuous. Time: 1 day. Significantly more difficult terrain, higher altitudes. Food, water and hiking equipment is necessary.
- Difficult hikes: they may last several days or weeks. They can be recommended only for well-prepared, experienced and healthy hikers. They need special equipment. Hikers visit places which are accessible only on foot. They spend the night(s) in tents or chalets.
Extreme sports in nature walking (an outline)
- Glacier tour. Winter equipment is a must.Hikers walk and climb in the world of eternal ice and snow. Hikers need the guidance of a hike master, too. Their equipment included mountaineering boots, ice axe, ropes, anchor, straps, mountaineering chair etc.
For further reading see: gleccsermászás,
http://www.fsz.bme.hu/mtsz/szakmai/zk20.htm
- Rock climbing: physically strnuous activity done on steep or even vertical rock wall. The mountaineering equipment is continuously developing and this improvement has made it possible to overcome extreme difficulties. Accident-free climbing has been made possible by using special chairs, ropes climbing harnesses and carabiners. Theoretical knowledge and practical climbing skills are all essential to become a good climber.
For further details see the links below: equipment: (http://www.petzl.com/en/Sport#.VfrdRxGqqko), rock climbing in Hungary (http://mhssz.hu/hegymaszo-szakag/maszoiskolak-korlatozasok-engedelyek), indoor wall climbing in Hungary (http://massz.hu/maszohelyek/magyarorszagi-maszotermek), difficulty scale (http://massz.hu/hasznos/nehezsegi-skalak), picture.
- via ferrata (klettersteig): its most important characteristic feature is the steep nature of the terrain that creates the need for some form of protected paths, while the presence of ledges and natural weaknesses means relatively easy but rewarding routes can often be created. On these ledges there are special via ferrata devices that help climbers. The essence of a modern via ferrata is a steel cable which runs along the route and is periodically fixed to the rock. Climbers can secure themselves to the cable, limiting any fall.
For further reading see: equipment, French information leaflet (http://www.chamonix.net/english/mountaineering/via-ferrata),
- water sportsi: hydrospeed, rafting, canyoning, etc.
- Air sports: paragliding, hang gliding (https://hu.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sikl%C3%B3erny%C5%91), (https://hu.wikipedia.org/wiki/S%C3%A1rk%C3%A1nyrep%C3%BCl%C5%91), stb.
Different devices are used by tourists to enjoy the time spent in nature to the maximum. On the basis of the above there are different types of hikes. When choosing which type to be engaged in, the length of the time available, our financial possibilities, the seasonality of the sport, our personal interests and mental and physical preparedness play a role
Specialized hikes (http://www.fsz.bme.hu/mtsz/szakmai/zk20.htm):
- Walking tours (fénykép természetjáró)
- Cycling tours (fénykép kerékpártúra)
- Rowing tours
- Caving tours
- Mountaineering tours (fénykép sziklamászás)
- Skiing tours (fénykép sí tábor)
- other
The ten commandments of hikers
- Prepare carefully!
- Plan your hike considering your physical abilities and level of experience!
- Dress functionally, comfortably and modestly!
- Walk around with open eyes and ears. Open your heart to the beauty of nature!
- Be quiet and disciplined. Be a guest!
- Keep hiking rules and make other people keep them, too ( how to build a fire, waste disposal, toilets, camping, protected areas, guided tours).!
- After leaving restore everything to its original state. (campsite, hostel, toilets) !
- Love and protect nature. Make other people respect it, too!
- Respect your fellow hikers and never leave them in trouble!
10. Utilize in everyday life what you have learnt from nature!
Requirements of hike masters
- High level of knowledge through training and in-service training programs,
- Leadership skills excellent teaching social and communication skills
- Experience, physical preparedness, good health.
A hike master can
- Plan and lead hikes, modify plan, give orders to participants, wan them and exclude them form the hike if it is a necessity.
- Duties: lead the hike as well as he can, lifelong learning and training (intellectual, physical)
- Responsibilities: familiarity with legal background, rules and regilations. Keeping them and making other people keep them.
Hiking plan and organization of hikes
- choosing a hike master,
- decision on group composition
- determining the goal(s)
- consideration of the season, weather factors, recruiting helpers, accident-free accomplishments
- itinerary, deciding on checkpoints.
- Surveying the possibilities of using technical devices, sport equipment, orientation devices, maps etc.
- Calculating costs. The amount is dependent on successful projects, other sources, supporters.
- Transport information. How to get to the start point? Where to park? How to get back to the meeting point?
- Accomodation possibilities,
- Acquisition of permissions to enter protected areas. Warning of dangers.
- Information, data collection concerning expected problems and difficulties, dangerous situations.
- Compilation of hiking plan, scheduling, draft itinerary, time allotted, sights, rest areas, time reserve
- Other issues: ID cards, registration etc.
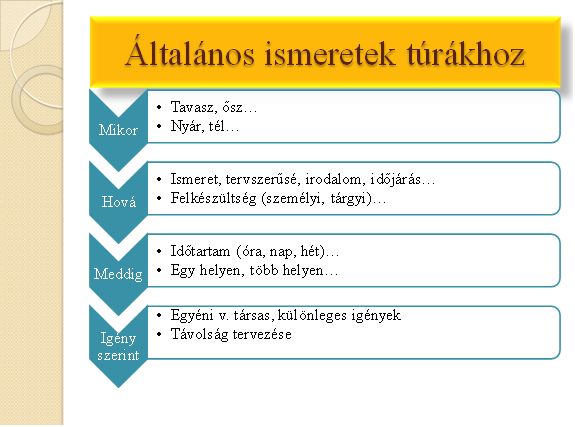
Figure 2,Summary of organizational tasks (own source)
When? Spring, autumn, summer, winter…..
Where? Experience, literature, weather
Preparedness: personal, knowledge of facts
From what time to what time? Length (hours, days, weeks)
One site, several sites
Special needs: individual or group special needs , planning the distance.
Leading the hike:
- Registration of participants at meeting point. Survey of health issues. Briefing.
- Rules. Order of hikers. Recommended speed, distance to be kept between hikers, number and length of rests, walking uphill or downhill, sights, waste treatment, fire building rules, first aid. Treatment of minor injuries, correction of itinerary, evaluation, discussion.
- After-hike documentation, reporting
- Recommended equipment: either provided by participants or hike master.
During hike pay attention to the following:
- Animals, plants, insect bites
- Possible dangers of swimming or sunbathing,
- Edible and poisonous plants.
- Using the toilet, hygienic rules.
- Unexpected events, injuries, faulty equipment etc..
- Know and apply first aid techniques.
Surveying the area
Considering the natural environment and its characteristics.
- Geographical location
- The size and horizontal and vertical dimensions of the area.
- The terrain, rock morphology.
- The geographic structure of the terrain, its typical features: mountains, plains, valleys, hills etc.
The climatic features of the area.
The amount and distribution of precipitation. Presentation 1.
Wind. presentation 2
(http://old.eumet.hu/0-gfs/gfs.php?domain=mo&terkepszam=61&terkeptipus=21).
- Temperatures, microclimate ( canyons and caves),
- ·Weather forecast prezentation 3
(http://koponyeg.hu/t/Szeged).
- ·Hydrological features of the area presentation 4
(http://www2.kdtvizig.hu/hu/balaton).
- Properties of the soil
- Typical flora and fauna, protected species, ’immigrant’ species, new plants, destroyed habitats, (clearings, refuse dumps)
- Protected areas, level of protection, types of protected areas presentation 5 (https://www.bfnp.hu/magyar/oldalak/kis_balaton/1/1).
- Degree of inhabitation, distribution of inhabitants, typical population groups, nationalities, minorities
- Types of settlements, expected services (accomodation, meals, shopping), sights (museums, churches, castles etc.), opportunities for doing sport (swimming pool, sports ground etc. )
- Transport network, accessibility,
- Ethnographical characteristics: architecture, agriculture, arts and crafts, gastronomy, special features,
- Architecture, (settlement structure): castles, castle ruins, churches, mansions, market place, main square.
- Historical mementos: castle ruins, battlefields
- Religious characteristics: places of pilgrimage, holy places, chapels, churches etc.