Csaba Varga, PhD, Anikó Pósa, PhD, Krisztina Kedvesné Kupai: The metabolic syndrome
III.3.C. Effects of catecholamines
Catecholamines such as E and N are responsible for various sympathetic effects on the nervous system.
They are released from the adrenal gland medulla, the sympathetic ganglia and the neurons
Their main effects: BP ![]() ,
,
heart function ![]() ,
,
breathing ![]() ,
,
blood Glu level ![]() ,
,
food intake ![]() ,
,
levels of glucocorticoids ![]() .
.
They have roles in the physiology of behavioral responses to danger, and in Cannon’s alarm reaction (Fig. 6), which describes the main effects of these hormones.
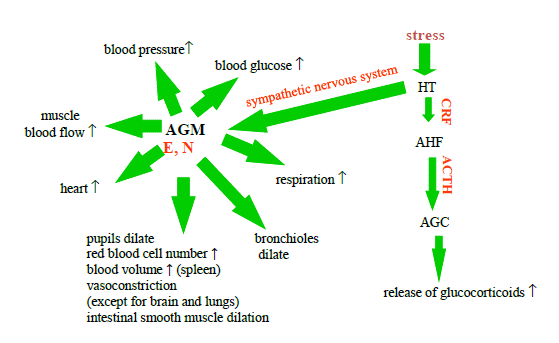
Figure 6. Cannon’s alarm reaction
(CRF = Corticotropic-releasing factor, ACTH = adrenocorticotropic hormone, AGC = adrenal gland cortex, AGM = adrenal gland medulla, HT= hypothalamus, AHF=Adenohypophysis, E=Epinephrine, N=Norepinephrine)