

TÁMOGATÁS:
Jelen tananyag a Szegedi Tudományegyetemen készült az Európai Unió támogatásával. A pályázat címe: A Szegedi Tudományegyetem készségfejlesztő és kommunikációs programjainak megvalósítása a felsőoktatásba való bekerülés előmozdítására és az MTMI szakok népszerűsítésére. Pályázati azonosító: EFOP-3.4.4-16-2017-00015
LEÍRÁS: Az alábbi tananyagrészlet az "Algoritmusok és adatszerkezetek az alkalmazásfejlesztésben” témához kapcsolódóan, leírásokokon és példaprogramokon keresztül mutatja be, hogy hogyan tudjuk alkalmazni az algoritmikus gondolkodást és algoritmizálási ismereteinket az alkalmazásfejlesztésben, konkrétan a JavaScript és VueJS-SFC szintaxis felhasználásával, komplex alkalmazási példákkal segítve a tanárok munkáját. TARTALOMJEGYZÉK (feladatleírás és munkaterv alapján)
# 4. Fejezet: Algoritmusok és adat-szerkezetek a szoftverfejlesztésben
# 4.1. Algoritmikus problémák, keresés, rendezések
Beszúró rendezés T tombben az elemek, helyben rendezés
function minindex(i,n) {
min=T[i] ;
mindex=i ;
for ( j=i+1; j<=n; j++ ) {
if ( T[j] < min ) {
min = T[j] ;
mindex = j ;
}
}
return mindex ;
}
function cserehakell(i,j) {
if (T[i]>T[j]) { a:=T[i] ; T[i]:=T[j] ; T[j]:=a ; }
}
for (i=1;i<n;i++) cserehakell( i, minindex(i+1,n) ) ;
# 4.2. Alapvető adatszerkezetek
# Verem, Sor, Prioritási sor, Kupac
<template>
<div id="conta">
<select v-model="type">
<option value="1">Verem</option>
<option value="2">Sor</option>
<option value="3">Prioritási sor</option>
</select>
<hr>
<h3></h3>
<input v-model="elem"
v-if="type==1"
@keyup.enter="verem.put(elem),elem=''"
placeholder="Betesz a verembe" />
<input v-model="elem"
v-if="type==2"
@keyup.enter="sor.put(elem),elem=''"
placeholder="Betesz a sorba" />
<input v-model="elem"
v-if="type==3"
@keyup.enter="prisor.put(elem),elem='',rajz()"
placeholder="Betesz a prioritási sorba" />
<br>
<button v-if="type==1 && verem.size"
@click="kivett.push(verem.get())"
>Kivesz a veremből</button>
<button v-if="type==2 && sor.size"
@click="kivett.push(sor.get())"
>Kivesz a sorból</button>
<button v-if="type==3 && prisor.size"
@click="kivett.push(prisor.get()),rajz()"
>Kivesz a prioritási sorból</button>
<hr>
<table class="s">
<tr><th>Konténerek</th></tr>
<tr v-for="(container,i) in [
verem.container,
sor.container,
prisor.container,
kivett
]">
<td><b>{{ aszlist[i] }}</b></td>
<td v-for="elem in container"
class="sor">{{ elem }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<span v-if="prisor.container.length>1 &&
prisor.container.length<100">
<br>
<div><b>Kupac ábrázolása:</b></div>
<br>
<div id="mynetwork"></div>
</span>
<hr>
<a href="Adatszerk_forras.html">Forráskód</a>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import vis from 'vis'
var nodes=[], edges=[], container, data, options, network
function drawgraph(p1, p2) {
nodes = new vis.DataSet(p1)
edges = new vis.DataSet(p2)
container = document.getElementById('mynetwork')
data = { nodes, edges }
options = {
layout: {
hierarchical: {
sortMethod: "directed"
}
},
nodes: {
shape: 'box',
fixed: true,
font: {
color: '#000',
size: 36, // px
face: 'Niramit',
background: 'none',
strokeWidth: 0, // px
strokeColor: '#ffffff',
align: 'center',
multi: false,
vadjust: 0
},
color: {
border: '#333333',
background: 'rgb(190, 237, 242)',
highlight: {
border: '#2B7CE9',
background: '#42B5BF'
}
}
},
edges: {
arrows: {
to: {enabled: true, scaleFactor: 0.8, type:'arrow'}
},
arrowStrikethrough: false,
chosen: true,
color: {
color:'#444444',
highlight:'#ed4576',
hover: '#848484',
inherit: 'from',
opacity: 1
},
dashes: false
}
}
network = new vis.Network(container, data, options)
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.container = [], this.size = 0
}
put(x) {
if (Array.isArray(x)) {
x.forEach(element => {
this.container.push(element),
this.size++
})
} else {
this.container.push(x), this.size++
} //O(1)
}
get() { // O( 1 )
if (this.size) {
this.size--
return this.container.pop() // O( 1 )
} else return null
}
check() {
return this.container[0] // O( 1 )
}
toarray() { // O( n * get() )
let rv = []
while (this.size)
rv.push(this.get())
return rv
}
[Symbol.iterator]() { // O( n * get() )
return {
next: () => {
if (this.size > 0) {
return {
value: this.get(),
done: false
}
} else {
return {
done: true
}
}
}
}
}
}
class BadQueue extends Stack {
constructor() {
super()
this.offset = 0
}
get() { // O( n )
if (this.size) {
this.size--
return this.container.shift() // O( n )
} else return null
}
}
class Queue extends Stack {
constructor() {
super()
this.offset = 0
}
get() { // O( 1 )
if (this.size) {
this.size--
let elem = this.container[this.offset++]
if (this.offset * 2 >= this.container.length) {
this.container = this.container.slice(this.offset)
this.offset = 0
}
return elem // O( 1 )
} else return false
}
check() {
return this.container[this.offset] // O( 1 )
}
}
class PQueue extends Stack {
put(x) { // O(1) / element
if (Number(x)==x) x=Number(x)
if (Array.isArray(x)) {
x.forEach(element => {
this.container.push(element), this.fix(this.size++)
})
} else {
this.container.push(x), this.fix(this.size++)
}
}
get() { // O(log n)
if (this.size) {
let ret = this.container[0]
if (--this.size) {
this.container[0] = this.container.pop()
this.fixup(0)
} else this.container.pop()
return ret
} else return null
}
fixup(p) { // O(log n)
let q1 = ( p + 1 ) * 2 ,
q2 = q1 - 1,
q = 0
if (q1 > this.size + 2) q1 = p
if (q2 > this.size + 2) q2 = q1
this.container[q1] > this.container[q2] ? q = q1 : q = q2
console.log(this.container[q1],this.container[q2],q)
if (p != q) {
this.cshn(q, p), this.fixup(q)
}
}
fix(p) { // O(log n)
let q = Math.round( (p+1) / 2 - 0.4 ) - 1
this.cshn(p, q)
if (q > 0) this.fix(q)
}
cshn(a, b) { // O(1)
if ( this.container[a] > this.container[b] )
[ this.container[a], this.container[b] ] =
[ this.container[b], this.container[a] ]
}
}
export default {
data: () => ({
aszlist: ['verem','sor','prioritási sor','helyi konténer'],
type: 3,
elem: '',
kivett: [],
verem: new Stack,
sor: new BadQueue,
prisor: new PQueue,
nodes, edges
}),
methods: {
rajz() {
nodes=[];
edges=[];
this.prisor.container.forEach( (v,i) => {
nodes.push({ id: i+1, label: `${ v }` })
} );
this.kupac(1);
if (nodes.length>2 && edges.length)
drawgraph(nodes, edges );
this.nodes=nodes;
this.edges=edges;
},
kupac(i) {
if (2*i<=nodes.length) {
edges.push( { from: i, to: 2*i } );
this.kupac(2*i)
};
if (2*i<nodes.length) {
edges.push( { from: i, to: 2*i+1 } );
this.kupac(2*i+1)
};
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
div#conta {
input {
font-size: 20px;
padding: 5px;
width: 250px;
}
select {
font-size: 20px;
width: 250px;
}
button {
font-size: 20px;
width: 250px;
}
table.s {
border-collapse: separate;
border-spacing: 10px;
border:solid 1px #123456;
td {
background-color: rgb(190, 237, 242);
border: solid 1px black;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 5px;
}
}
div#mynetwork {
height:500px;
border: solid 1px black;
border-radius:10px;
box-shadow: 0 0 4px black;
}
}
</style>

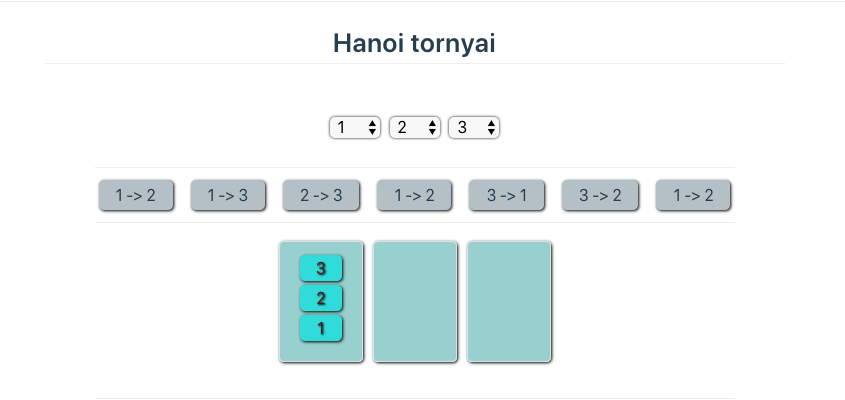
# 4.3. Rekurzióval megoldható problémák
# Hanoi Tororny példaprogram - VUE

<template>
<div class="main" name=hanoi>
<div class=i>
<select v-model.number="a" @change="hanoi()">
<option v-for="i in 3">{{i}}</option>
</select>
<select v-model.number="b" @change="hanoi()">
<option v-for="i in 3">{{i}}</option>
</select>
<select v-model.number="n" @change="hanoi()">
<option v-for="i in 13">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br>
<hr>
<div class="co"
:id="windowWidth>600
?'so'
:(windowWidth>300?'ko':'mo')">
<div v-if="elem!='! ! ! ! !'"
:id="i" @click="rak(elem,i)"
:key=i v-for="(elem,i) in mo.split(',')"
>{{ elem }}</div>
</div>
<hr>
<div class=i>
<table>
<td v-for="oszlop in t"
:style="`height: ${n*30+10}px;`">
<div v-for="korong in oszlop"
>{{korong}}</div>
</td>
</table>
</div>
<br>
<hr>
<a href="/~tnemeth/examples/algoexamples/Hanoi_forras.html"
>Forráskód</a>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { vueWindowSizeMixin } from 'vue-window-size'
const h = ( a, b, n ) => (
n < 2
? `${ a } -> ${ b }`
: `${ h( a, 6-a-b, n-1 ) },
${ a } -> ${ b },
${ h( 6-a-b, b, n-1 ) }`
)
export default {
name: 'hanoi',
mixins: [vueWindowSizeMixin],
data: () => ({
a:1, b:2, n:3, mo: '',
t: [[],[],[]]
}),
methods: {
rak(x,i) {
let jt=this.mo.split(',')
jt[i]="! ! ! ! !"
this.mo=jt.join(',')
var [i,j]=x.split(' -> ')
var le = this.t[i-1].pop()
if ( le!==undefined ) this.t[j-1].push( le )
this.$forceUpdate()
},
hanoi() {
if (this.a==this.b) {
this.a=1
this.b=2
}
this.t[this.a-1]=Array(this.n)
.fill(0)
.map((v,i) => this.n-i)
this.t[this.b-1]=[]
this.t[6-this.a-this.b-1]=[]
this.mo = this.n<14?h(this.a, this.b, this.n):'túl nagy az n'
}
},
mounted() {
this.hanoi()
}
}
</script>
<style lang=scss scoped>
div.main {
text-align: center;
div.i {
text-align: center;
}
margin: 50px;
select {
width: 50px;
font-size: 16px;
margin: 3px;
border-radius: 9px;
border: none;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 3px black;
}
div.co {
text-align: center;
display: grid;
grid-column-gap: 10px;
grid-row-gap: 10px;
div {
white-space: nowrap;
background-color: rgb(182, 191, 199);
padding: 6px;
margin: 4px;
cursor:pointer;
user-select: none;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
}
div#so {
grid-template-columns: repeat(7,auto);
}
div#ko {
grid-template-columns: repeat(3,auto);
}
div#mo {
grid-template-columns: repeat(2,auto);
}
table {
text-align: center;
border-collapse: separate;
margin: 0 auto;
display: table;
border-spacing: 10px;
}
td {
width: 50px;
text-align:center ;
vertical-align: top;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px black;
border-radius: 5px;
background-color: rgb(164, 208, 207);
div {
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px black;
border-radius: 5px;
padding :4px;
margin: 4px;
background-color: rgba(111, 220, 218, 90);
color: rgb(77, 19, 23);
text-shadow: 1px 1px 2px black;
}
}
}
</style>
# Példa rekurzió alkalmazására - Aknakereső játék - VUE
<template>
<div id="app">
<table class="t1" @click.right.stop.prevent>
<tr v-for = "(row,y) in table">
<td v-for = "(cell,x) in row"
@click.exact = "lclick(x,y)"
@click.alt.exact = "rclick(x,y)"
@click.ctrl.exact= "rclick(x,y)"
@click.right.stop.prevent= "rclick(x,y)"
v-html="cell==='O'?'💣':cell==='B'?'<big>⚑</big>':cell"
:class="'p'+cell"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=10 class="blank"></td>
</tr>
<tr v-if="!nyert">
<td colspan=2 class="text">Mód:</td>
<td class="pB" v-if="!bmode" @click="bmode=true">⚑</td>
<td v-if="bmode" @click="bmode=false"> </td>
<td colspan="7" class="text">
<span v-if="!bmode"
@click="bmode=true"
> ⇦ vedd fel a bombajelölőt! </span>
<span v-else
@click="bmode=false"
> ⇦ tedd le a bombajelölőt! ⇧ </span>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<span v-if="nyert===1">
<br>
<div class="nyert">Nyertél!</div>
</span>
<span v-if="nyert===-1">
<br>
<div class="vesztett">Vesztettél!</div>
</span>
<div class="btc">
<br>
<div v-if="nyert"
@click="createtable()"
class="btn">Új játszma</div>
</div>
<hr>
<a href="/~tnemeth/examples/webexamples/Aknakereso_forras.html">
Forráskód
</a>
</div>
</template>
<script>
let masz, tilt, xp, yp, hba
export default {
name: 'aknak',
data() {
return {
n:10, m:10, asz: 14, nyert: 0, bmode: false,
table: [],
aknak: 0
}
},
mounted() {
this.createtable()
},
methods: {
createtable() {
hba = new Set()
this.aknak = new Set()
this.nyert=0
masz=0
tilt=0
let x, y
this.table=[]
for (let i=0;i<this.n;i++) {
let sor = []
for (let j=0;j<this.m;j++) sor.push(' ')
this.table.push(sor)
}
for (let i=0;i<this.asz;i++) {
do {
x = Math.trunc(Math.random()*this.n)
y = Math.trunc(Math.random()*this.m)
} while ( this.aknak.has(`${y}-${x}`) )
this.aknak.add(`${y}-${x}`)
}
},
lclick(x,y) {
if (this.bmode) {
this.rclick(x,y)
this.bmode=false
}
else if ( !this.nyert && this.table[y][x]==="B" ) {
this.rclick(x,y)
}
else if ( !this.nyert && this.table[y][x]===" " ) {
if (this.aknak.has(`${x}-${y}`) ) {
this.nyert=-1
Array.from(this.aknak).forEach( v => {
[xp, yp]=v.split('-')
if (this.table[yp][xp]===" ") this.$set(this.table[yp], xp, 'O')
})
Array.from(hba).forEach( v => {
[xp, yp]=v.split('-')
this.$set(this.table[yp], xp, 'H')
})
this.$set(this.table[y], x, 'O')
this.aknak.clear()
return false
}
let vsz=[-1,0,1], fl=vsz, count=0
vsz.forEach( v =>
fl.forEach( f => {
if (this.aknak.has(`${x+v}-${y+f}`)) count++
} )
)
this.$set(this.table[y], x, count)
if (count==0) {
vsz.forEach( v =>
fl.forEach( f => {
if (
typeof this.table[y+f] !== 'undefined' &&
this.table[y+f][x+v]===" "
) this.lclick(x+v,y+f)
} )
)
}
}
},
rclick(x,y) {
if ( !this.nyert && this.table[y][x]===" " ) {
this.$set(this.table[y], x, "B")
if ( this.aknak.has(`${x}-${y}`) ) masz++
else tilt++, hba.add(`${x}-${y}`)
if ( masz === this.asz && tilt===0 ) this.nyert=1
}
else if ( !this.nyert && this.table[y][x]==="B" ) {
if ( this.aknak.has(`${x}-${y}`) ) masz--
else tilt--, hba.delete(`${x}-${y}`)
this.$set(this.table[y], x, " ")
masz--
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang=scss scoped>
@import url('https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Roboto+Slab&display=swap');
.btc {
text-align: center;
}
.btn {
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 6px;
cursor:pointer;
background-color: #3a435c;
color:snow;
width:90px;
border-radius: 7px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px black ;
}
.btn:hover {
cursor:pointer;
background-color: #273048;
color:snow;
box-shadow: 0 0 2px black ;
}
.cx {
margin-left:10px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
#app {
font-family: 'Roboto Slab', serif;
user-select: none;
text-align: center;
color: #095d6c;
h2 {
text-shadow: 0px 0px 2px #19334d;
}
div#content {
text-align: center;
}
}
div.ujj {
margin:0px auto;
width: 90px;
cursor:pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px rgb(99, 97, 97);
}
div.ujj:hover {
background-color: #cfded9;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px rgb(34, 33, 33);
}
div.nyert {
font-size: 25px;
color:rgb(58, 147, 157) ;
font-weight: bold;
text-shadow: 0 0 2px rgb(138, 29, 29);
}
div.vesztett {
font-size: 25px;
color:rgb(213, 37, 34) ;
font-weight: bold;
text-shadow: 0 0 2px rgb(138, 29, 29);
}
table {
border-collapse: inherit;
display: table;
margin:0px auto;
border-spacing: 1px;
td {
text-align: center;
width: 28px;
height: 28px;
background-color: #e6f3ef;
border-radius: 4px;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px rgb(99, 97, 97);
cursor: pointer;
border: solid 1px rgb(29, 43, 75);
color:rgb(55, 6, 6);
padding:3px;
}
td.p0 { background-color: #afe9d8; }
td.p1 { background-color: #e6e9af; }
td.p2 { background-color: #f5d4a3; }
td.p3 { background-color: #ff9f9f; }
td.p4 { background-color: #fa8383; }
td.p5 { background-color: #f94343; color:white;}
td.pB {
background-color: #ffc3f6;
color:rgb(205, 73, 73);
font-weight: bold;
text-shadow: 0 0 2px rgb(0, 60, 255);
}
td.pH {
background-color: #9f0707;
color:snow;
font-weight: bold;
}
td.pO {
background-color: #a7a7a7;
color:rgb(240, 203, 203);
font-weight: bold;
}
td.text {
background-color: #cecece;
color:rgb(19, 90, 106);
font-weight: bold;
}
td.blank {
border:none;
background: none;
box-shadow: none;
height: 10px;
cursor: none;
}
}
</style>
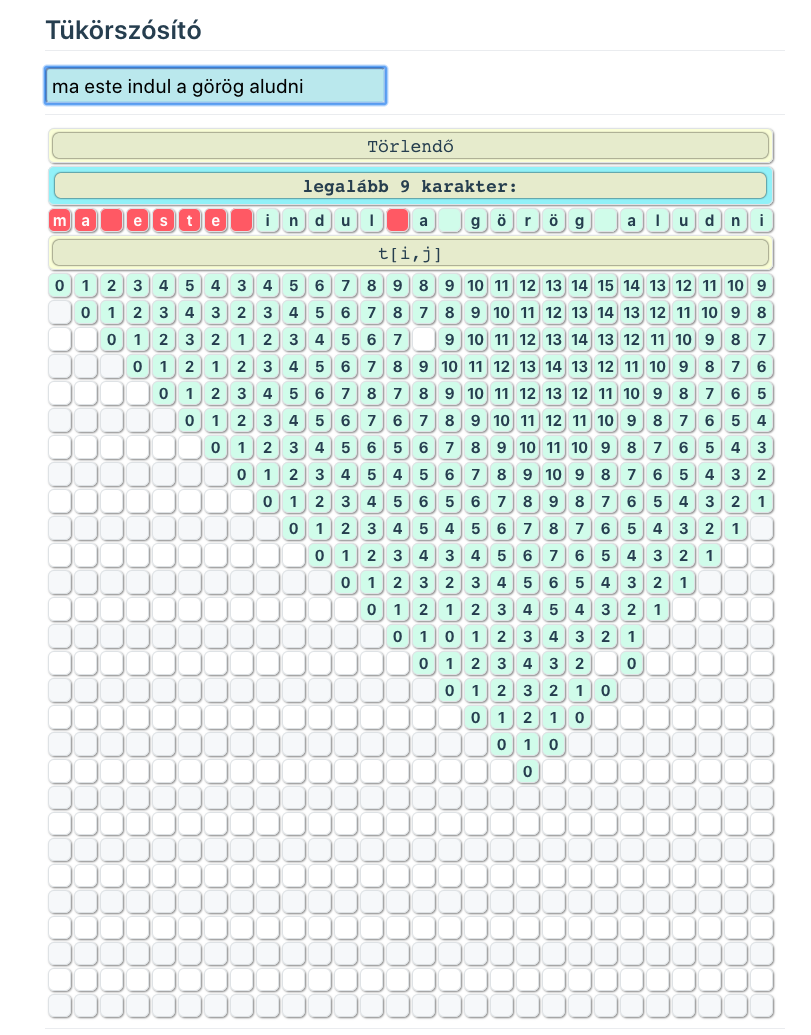
# 4.4. Dinamikus programozás
# Tükörszó probléma megoldása rekurzió - memorizálással

<template>
<div id=cont>
<div id=app>
<input v-model="s"
@keyup="szamol()"
placeholder="Szó / Szöveg"/>
<hr>
<table v-if="mi">
<tr><td class="szoveg"
:colspan="s.length"
title="A törlendő karakterek piros mezőben, az előállított tükörszó zöldben."
><pre>Törlendő</pre></td></tr>
<tr>
<td class="eredm" :colspan="s.length">
<pre>legalább {{ mi }} karakter:</pre>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td :class="el=='.'?'z':'x'"
v-html="el==='.'?s[i]:el"
v-for="(el,i) in mo"/>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="szoveg" :colspan="s.length">
<pre>t[i,j]</pre>
</td>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(row,j) in t">
<td :class="cell?'x':'o'"
:key="`${i}-${j}`"
v-for="(cell,i) in row">
{{ cell?cell-1:'' }}
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<div v-else>Ez tükörszó</div>
</div>
<hr>
<a href="/~tnemeth/examples/algoexamples/Tukorszo_forras.html">
A megoldás matematikai modelleje és forráskódja
</a>
</div>
</template>
<script>
let o = {
mi(i=0,j=this.s.length-1) {
return this.t[i][j] ? this.t[i][j] : i>=j ? this.t[i][j] = 1 :
this.s[i]===this.s[j] ? this.t[i][j] = this.mi(i+1,j-1) :
this.t[i][j] = Math.min(this.mi(i+1,j),this.mi(i,j-1))+1
},
mo(i=0,j=this.s.length-1) {
let s=this.s.split('')
do this.t[i][j-1]+1===this.t[i][j] ? s[j--]='.' :
this.t[i+1][j]+1===this.t[i][j] ? s[i++]='.' : ( i++, j-- )
while (this.t[i][j]-1)
return s.join('')
}
}
export default {
name: 'tsz',
data: () => ({
s: "",
mi: 0,
mo: "",
t: []
}),
methods: {
szamol() {
this.s=this.s.toLocaleLowerCase()
if (this.s.length) {
o.t = Array(this.s.length)
.fill()
.map(v=>Array(this.s.length).fill(0))
o.s=this.s
this.mi=o.mi()-1
this.mo=this.mi?o.mo():o.s
this.t=o.t
}
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
div#cont {
div#app {
font-size: 20px;
input {
background-color: rgb(196, 232, 238);
width: 327px;
font-size: 20px;
padding: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
}
table {
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
border-collapse: separate;
border-spacing: 3px;
display: table;
td {
text-align: center;
font-size: 15px;
padding: 2px;
width: 17px;
height: 17px;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 2px gray;
border-radius: 6px;
}
td.z {
background-color: rgb(235, 88, 98);
font-weight: bold;
color:snow;
}
td.x {
background-color: rgb(217, 252, 233);
font-weight: bold;
}
td.szoveg {
user-select: none;
cursor: default;
text-align: center;
background-color: rgb(251, 255, 212);
font-size: 18px;
width: 320px;
}
td.eredm {
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 4px;
background-color: rgb(169, 241, 249);
}
}
}
pre {
margin: 2px ;
padding: 0 ;
background-color: rgb(231, 235, 202);
box-shadow: 0 0 2px black;
}
</style>
# 4.5. Mohó stratégia
A mohó algoritmus algoritmus az a problémamegoldó módszer, amely a globális optimumot helyi optimumok kiválasztásával próbálja megtalálni. Ez például a pénzváltás problémájaként ismert feladatban azt jelenti, hogy mindig a legnagyobb elérhető címletet választjuk.
Általánosan öt pillérre támaszkodik:
- egy halmazból veszi a jelölteket, amelyekkel felállítja a megoldáshalmazt
- egy kiválasztó függvény, amely a legjobb jelöltet választja ki a megoldás reményében
- egy lehetőségvizsgáló függvény, amely megnézi, hogy egy jelölt alkalmas-e a megoldásra
- egy célfüggvény, amely egy értéket megoldásnak, vagy részleges megoldásnak jelöl
- egy megoldásfüggvény, amely jelzi, ha megtaláltuk a teljes megoldást.
A módszer jól alkalmazható néhány matematikai probléma megoldásában, de nem minden problémához garantálja az optimális megoldás megtalálását. Sokszor alkalmazzuk közelítő (approximációs módszerként is).
# 4.6. Gráfalgoritmusok
gráf mélységi és szélességi bejárása
<template>
<div id=id>
<button @click="mb(0)">Bejár</button>
<div v-for="(e,i) in mj"> {{i}} : {{e}}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
let g=[
[1,2],
[4,5],
[3],
[5],
[2],
[]
], i=1, p,
asz = {
adat: [],
betesz(p) {
this.adat.push(p)
},
kivesz() {
//return this.adat.shift() //szélességi
return this.adat.pop() //mélységi
}
}
export default {
data: () => ({
mj: Array(7).fill(0)
}),
methods: {
mb(p) {
this.$set(this.mj,p,i++) ;
asz.betesz(p) ;
while (asz.adat.length) {
p = asz.kivesz() ;
g[p].forEach( v => {
if (!this.mj[v]) {
this.$set(this.mj,v,i++) ;
asz.betesz(v) ;
}
})
}
}
}
}
</script>
# 4.7. Neurális hálózatok
Egy neurális hálózat egy idegrendszer vagy áramkör, vagy modern értelemben egy mesterséges ideghálózat, amely mesterséges idegsejtekből vagy csomópontokból áll. Így egy idegi hálózat vagy biológiai neurális hálózat, amely valódi biológiai neuronokból áll, vagy egy mesterséges idegi hálózat, amely a mesterséges intelligencia (AI) problémáinak megoldására szolgál. A biológiai neuron kapcsolatait súlyként modellezzük. A pozitív súly az gerjesztő kapcsolatot, míg a negatív érték a gátló kapcsolatot jelenti. Az összes bemenetet súlyokkal módosítják és összegezik. Ezt a tevékenységet lineáris kombinációnak nevezik. Végül egy aktiválási funkció vezérli a kimenet amplitúdóját. Például egy elfogadható kimeneti tartomány általában 0 és 1 közötti, vagy lehet -1 és 1.
Ezeket a mesterséges hálózatokat fel lehet használni prediktív modellezéshez, adaptív vezérléshez és alkalmazásokhoz, ahol adatkészlettel képesek tanulásra. A tapasztalatokból fakadó tanulás megtörténhet a hálózatokon belül, amelyek következtetéseket vonhatnak le egy összetett és látszólag független információhalmazból.