I.8.5. Ball handling techniques
1. Receiving the ball
Standing: In order to pass as soon as possible it is important to receive a pass on the forehand side. When the ball arrives at the backhand side, the player shall change the side for the sake of safer handling.
In the course of running: it is important to keep the momentum. The velocity of the player depends on the speed of the ball. It is important to avoid losing the verve, and using forehand and holding the ball is crucial. The upper body has to lean forward: as a result, the centre of gravity gets closer to the floor, and keeping the balance of the movement gets easier. The stick is on the side of the body, the receiving is started from there, preferably from the forehand side.
Receiving the ball approaching from the front: the stick is to be held at the side of the body with the knees slightly bent. Lowering the centre of gravity help receiving the ball on the forehand side. Ideally, the player does not need to watch the ball for a long time.
Ball coming from the side: the player moves forward, he/she has to reach slightly backwards with the stick, while leaning slightly backwards, putting one foot forward in order to maintain the continuity of the movement.
Ball coming from the back: it is best to try to turn around in order to receive the ball at the forehand side. If necessary, the ball can be received at the backhand side, but it is important to maintain continuity.
Receiving a high ball: after dodging the ball using the chest, it is best to receive it on the forehand side of the blade as soon as possible. If the ball travels at the height of the head, it can be caught from below.
Ball coming lower than waist: the player can get the ball with a direct leg movement, because it travels flatly. This move used as a direct pass provides advantage over the opponent. Only one kick is allowed.
2. Passes
Forehand and backhand low passes: the strength of the pass has to be chosen well so that the teammate is able to receive the ball in the safest way possible and to take advantage over the opponent. Backhand hits have the advantage that they make the pass less predictable, but forehand passes are still safer.
Forehand and backhand high passes: moderately high passes may be hit when the opponent makes low passes impossible. In this case, the shaft and the blade have to lean towards the body in order to achieve the perfect lift.
Pass-types according to direction:
- Forward
- Backward
- Side
Exercises in the video below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qmP_Lf8tuSQ
3. Dribbling
Dribbling is indispensable in floorball, because the player that is good at running with the ball and keeping it, draws the attention of one or two players from the opponent team, while with a proper pass they can be to the advantage of their team.
4. Shots on goal
Hit shot: the travelling ball can be hit using either the forehand or the backhand side of the blade. Players can take advantage of the gravity of their body in order to take the most powerful shot possible. In this case, the body leans sideways and forward more than at other times to exploit the body weight more. The hit consists of 3 phases: the back-swing, the hit and the follow-through. Before a backhand-shot, it is best to turn one’s back a bit against the goal, while the ball has to be next to the body. In this case, it is not necessary to use the weight of the body, the shot should rather be fairly straight.
Dragged shot: when shooting on the goal, the needed strength of the shot is achieved by having the ball always within the shaft of the stick, dragging the ball beside the body using the body weight. There are two phases of this shot: the beginning of the dragging and the follow-through.
Exercises in the video below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XvCBIMJvuO4
5. Fakes
As in many other sports, fakes are important in floorball, too, because teams can gain advantage from them and they can confuse the opponent.
Movement fakes: When keeping the ball firmly the players may confuse and intimidate the opponents using sudden movements and fakes and take advantage of the confusion. Different speeds of running and sudden changes in directions can also be of great use.
Fakes of passes and shots: the defending player can be confused by dribbling using the blade and trying to choose one safe passing route and then another one. Fake shot is best applied in front of the goal during the phase of the back-swing. This way, the goalkeeper or the defender moves a bit, providing an opportunity for a pass or a hit shot.
6. Defence techniques
Blocks: on-site block is best used in the moment of the free-hit. When the ball is passed in-movement block needs to be applied. The ball may be blocked using the stick or – depending on the height – stopped by body. Body-blocking can be done putting one knee on the ground, especially with low shots that can be stopped more likely this way.
Tackling: the movement that aims to catch the ball is called tackling. In order to seize the ball from the opponent, the player has to follow his/her moves. Tackling can be done by dragging the ball away from the opponent (except when it is on his/her blade) or by disturbing the player until he/she gives the ball away, and as soon as this happens the ball can be dragged or hit away from him/her. It is important not to break the rules during tackling. The best tackling is fast, decisive and properly aggressive, and the main goal is to prevent the players of the opponent team from attacking.
Body contact: in floorball only shoulder-to-shoulder contact is allowed. When trying to catch and keep the ball, a player may push against a player of the opponent team. There are rules sanctioning the violent and dangerous contacts.
7. Goalkeeper techniques:
The goalie, as opposed to the goalkeepers in other games, does not stand on their feet but on their knees. Upper arms are held horizontally, lower arms are held vertically. Shins are turned against each other, feet are closed in.
Position: the goalkeepers have to position themselves according to the movement of the ball. If the goalie is on the left side, he/she has to guard the short side, standing beside the goalpost and watching the shots aimed at the long side.
8. Technical skills:
The main objective is to learn how to control the ball and handle the stick. During training, the coach shows the direction with their hand, and the players move in that direction:
- When the coach holds their hands in either direction, the players have to move in that way.
- When the coach points at the players, they have to move backwards.
- When the coach blows the whistle, the players have to do a 5 m rush, then return to their places.
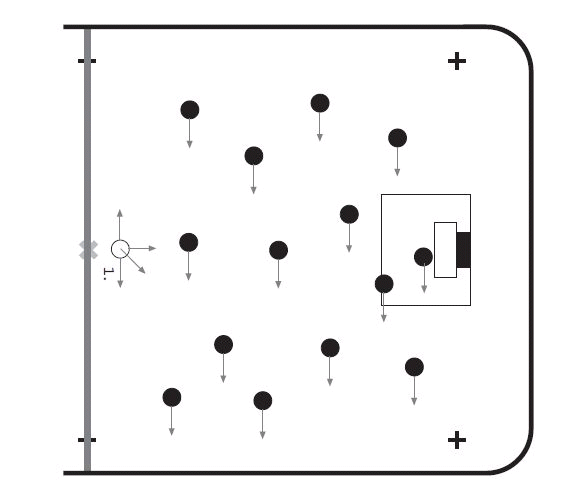
- Dribbling between the cones doing specific exercises. (360 degree turns around the cone; passing only the ball round the cone; tricks in front of cones)
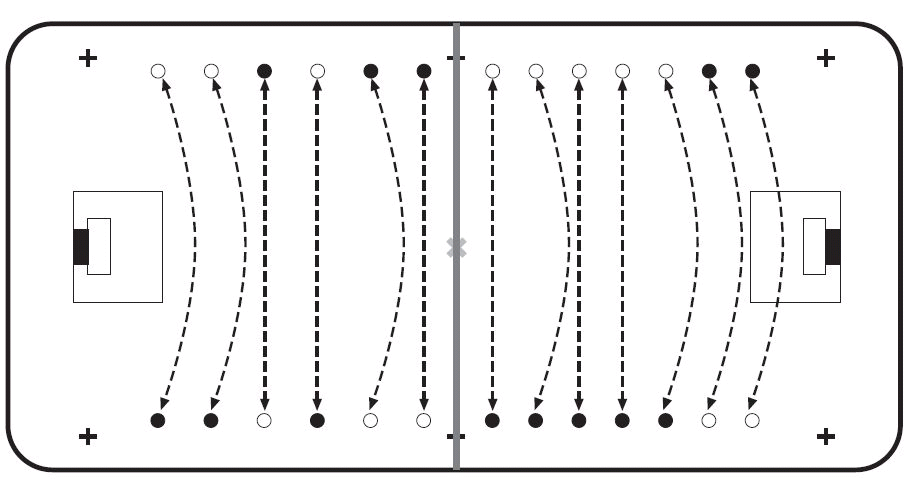
9. Exercises for passing
The main objective is to execute precise and smooth passes:
- First, pairs need to be formed taking a position as seen in the picture below.
- Pairs drill different forms of passing.
- In the beginning, they pass from a short distance, then the distance is increased.
- Players drill how to stop high passes using their body.
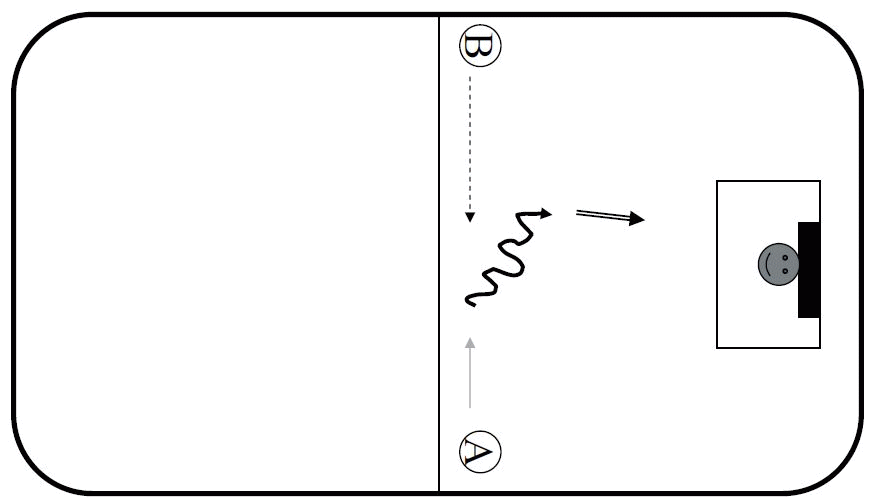
10. Receiving the ball and shooting
The main objective is to learn how to shoot and receive the ball when running. Technically proper execution leads to 1:1 game. The game starts from the centre by a pass, then the player passing becomes the defender while the former receiver has to lead a successful attack.
Exercises in the video below: